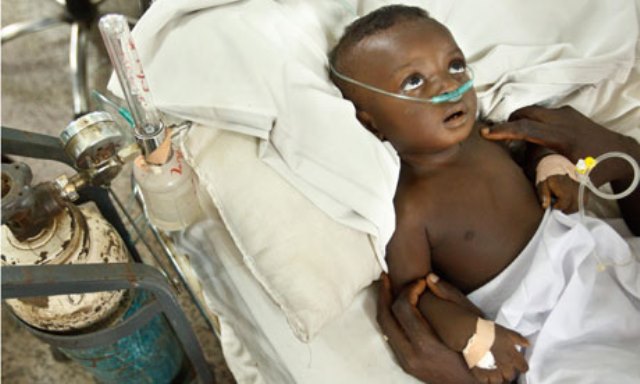
- Pneumonia accounts for 15% of all deaths of children under 5 years old, killing an estimated 922 000 children in 2015.
- Pneumonia can be caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi.
- Pneumonia can be prevented by immunization, adequate nutrition and by addressing environmental factors.
- Pneumonia caused by bacteria can be treated with antibiotics, but only one third of children with pneumonia receive the antibiotics they need.
Pneumonia is a form of acute respiratory infection that affects the lungs. The lungs are made up of small sacs called alveoli, which fill with air when a healthy person breathes. When an individual has pneumonia, the alveoli are filled with pus and fluid, which makes breathing painful and limits oxygen intake.
Pneumonia is the single largest infectious cause of death in children worldwide. Pneumonia killed an estimated 922 000 children under the age of 5 in 2015, accounting for 15% of all deaths of children under five years old. Pneumonia affects children and families everywhere, but is most prevalent in South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Children can be protected from pneumonia, it can be prevented with simple interventions, and treated with low-cost, low-tech medication and care.
Causes
- Pneumonia is caused by a number of infectious agents, including viruses, bacteria and fungi. The most common are:
- Streptococcus pneumoniae – the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia in children;
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) – the second most common cause of bacterial pneumonia;
- respiratory syncytial virus is the most common viral cause of pneumonia;
- in infants infected with HIV, Pneumocystis jiroveci is one of the commonest causes of pneumonia, responsible for at least one quarter of all pneumonia deaths in HIV-infected infants.
Transmission
Pneumonia can be spread in a number of ways. The viruses and bacteria that are commonly found in a child’s nose or throat, can infect the lungs if they are inhaled. They may also spread via air-borne droplets from a cough or sneeze. In addition, pneumonia may spread through blood, especially during and shortly after birth. More research needs to be done on the different pathogens causing pneumonia and the ways they are transmitted, as this is of critical importance for treatment and prevention.
Presenting features
The presenting features of viral and bacterial pneumonia are similar. However, the symptoms of viral pneumonia may be more numerous than the symptoms of bacterial pneumonia. In children under 5 years of age, who have cough and/or difficult breathing, with or without fever, pneumonia is diagnosed by the presence of either fast breathing or lower chest wall indrawing where their chest moves in or retracts during inhalation (in a healthy person, the chest expands during inhalation). Wheezing is more common in viral infections.
Very severely ill infants may be unable to feed or drink and may also experience unconsciousness, hypothermia and convulsions.
Risk factors
While most healthy children can fight the infection with their natural defences, children whose immune systems are compromised are at higher risk of developing pneumonia. A child’s immune system may be weakened by malnutrition or undernourishment, especially in infants who are not exclusively breastfed.
Pre-existing illnesses, such as symptomatic HIV infections and measles, also increase a child’s risk of contracting pneumonia.
The following environmental factors also increase a child’s susceptibility to pneumonia:
- indoor air pollution caused by cooking and heating with biomass fuels (such as wood or dung)
- living in crowded homes
- parental smoking.
Treatment
Pneumonia should be treated with antibiotics. The antibiotic of choice is amoxicillin dispersable tablets. Most cases of pneumonia require oral antibiotics, which are often prescribed at a health centre. These cases can also be diagnosed and treated with inexpensive oral antibiotics at the community level by trained community health workers. Hospitalization is recommended only for severe cases of pneumonia.
Prevention
nity level by trained community health workers. Hospitalization is recommended only for severe cases of pneu
Preventing pneumonia in children is an essential component of a strategy to reduce child mortality. Immunization against Hib, pneumococcus, measles and whooping cough (pertussis) is the most effective way to prevent pneumonia.
Adequate nutrition is key to improving children’s natural defences, starting with exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life. In addition to being effective in preventing pneumonia, it also helps to reduce the length of the illness if a child does become ill.
Addressing environmental factors such as indoor air pollution (by providing affordable clean indoor stoves, for example) and encouraging good hygiene in crowded homes also reduces the number of children who fall ill with pneumonia.
In children infected with HIV, the antibiotic cotrimoxazole is given daily to decrease the risk of contracting pneumonia.
Economic costs
The cost of antibiotic treatment for all children with pneumonia in 66 of the countdown to 2015 countries for maternal, newborn and child survival is estimated at around US$ 109 million per year. The price includes the antibiotics and diagnostics for pneumonia management.
WHO response
The WHO and UNICEF integrated Global action plan for pneumonia and diarrhoea (GAPPD) aims to accelerate pneumonia control with a combination of interventions to protect, prevent, and treat pneumonia in children with actions to:
- protect children from pneumonia including promoting exclusive breastfeeding and adequate complementary feeding;
- prevent pneumonia with vaccinations, hand washing with soap, reducing household air pollution, HIV prevention and cotrimoxazole prophylaxis for HIV-infected and exposed children;
- treat pneumonia focusing on making sure that every sick child has access to the right kind of care — either from a community-based health worker, or in a health facility if the disease is severe — and can get the antibiotics and oxygen they need to get well;
A number of countries including Bangladesh, India, Kenya, Uganda and Zambia have developed district, state and national plans to intensify actions for the control of pneumonia and diarrhoea. Many more have integrated diarrhoea and pneumonia specific action into their national child health and child survival strategies. For many countries the post Millenium Development Goal agenda has explicitly included ending preventable diarrhoea and pneumonia deaths as a priority action.
Courtesy: WHO